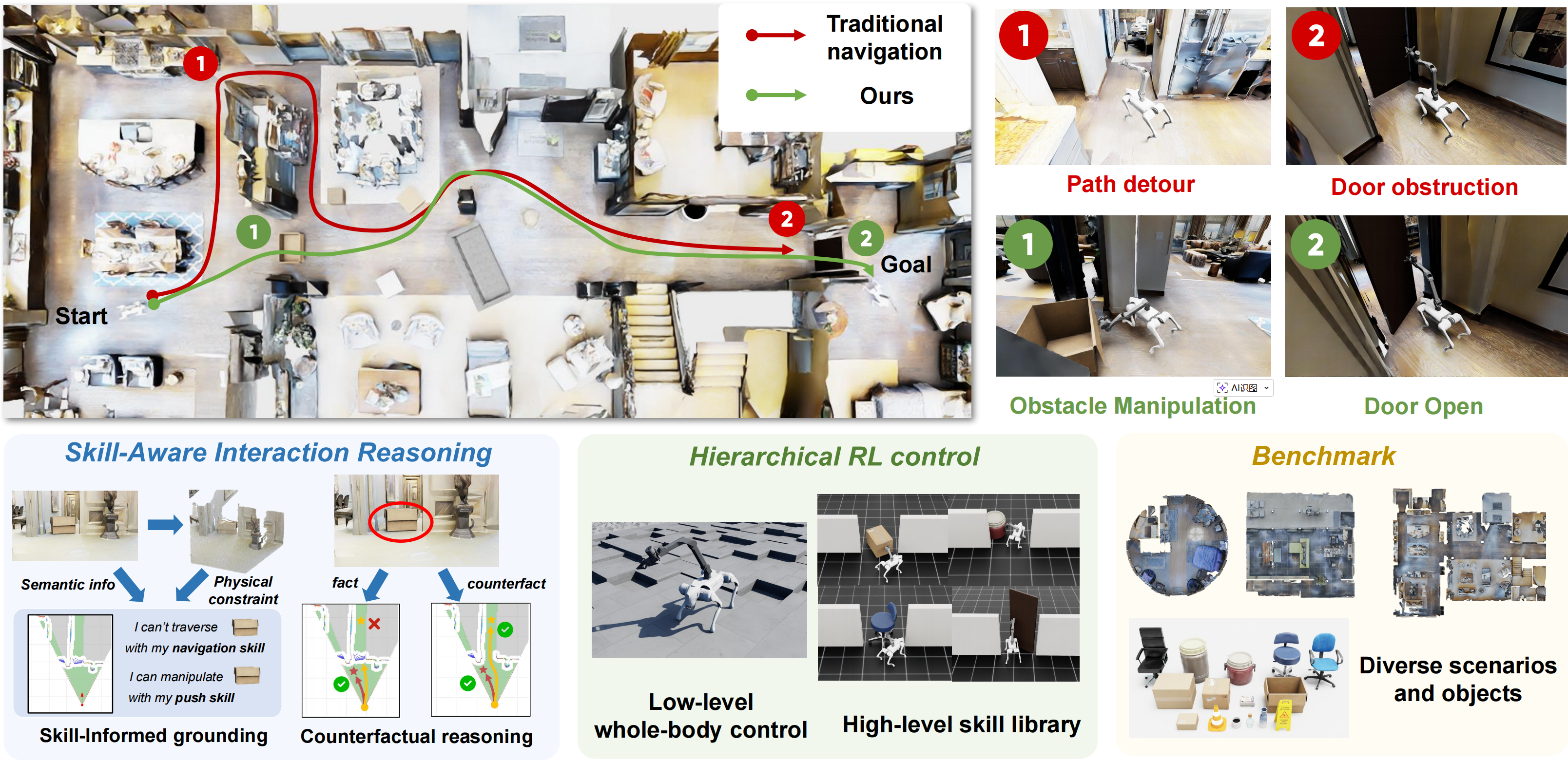
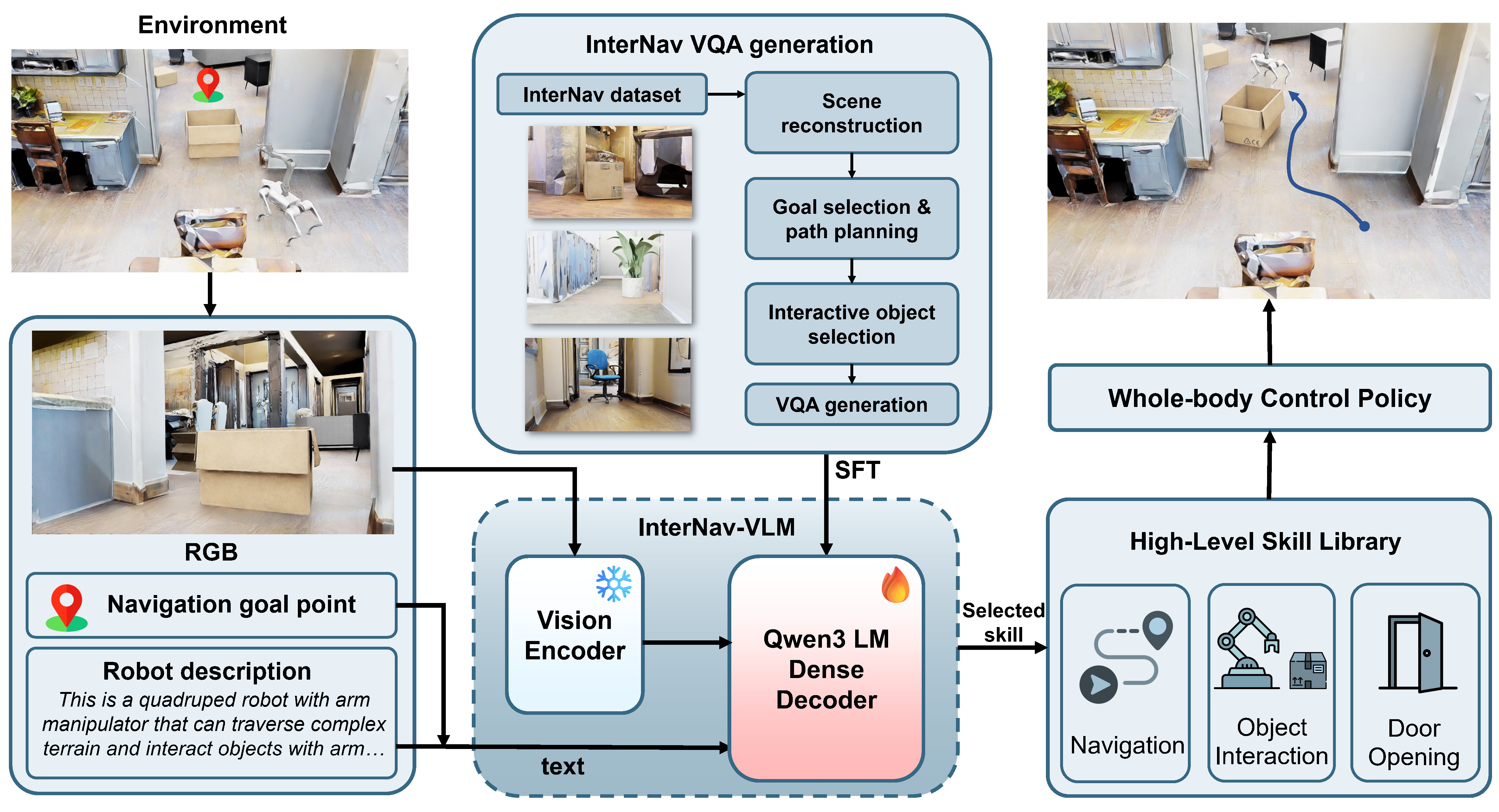
Recent vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in robotic planning. However, they typically function as semantic reasoners, lacking an intrinsic understanding of the specific robot’s physical capabilities. This limitation is particularly critical in interactive navigation, where robots must actively modify cluttered environments to create traversable paths. Existing VLM-based navigators are predominantly confined to passive obstacle avoidance, failing to reason about when and how to interact with objects to clear blocked paths. To bridge this gap, we propose Counterfactual Interactive Navigation with Skill-aware VLM (CoINS), a hierarchical framework that integrates skill-aware reasoning and robust low-level execution. Specifically, we fine-tune a VLM, named InterNav-VLM, which incorporates skill affordance and concrete constraint parameters into the input context and grounds them into a metric-scale environmental representation. By internalizing the logic of counterfactual reasoning through fine-tuning on the proposed InterNav dataset, the model learns to implicitly evaluate the causal effects of object removal on navigation connectivity, thereby determining interaction necessity and target selection. To execute the generated high-level plans, we develop a comprehensive skill library through reinforcement learning, introducing traversability-oriented strategies to manipulate diverse objects for path clearance. A systematic benchmark in Isaac Sim is proposed to evaluate both the reasoning and execution aspects of interactive navigation. Extensive simulations and real-world experiments demonstrate that CoINS outperforms existing baselines, surpassing the success rate by 17% overall and over 80% in complex long-horizon scenarios, while exhibiting robust generalization across diverse object categories and robot embodiments.